What is Zinc Melting Point? Facts and Figures
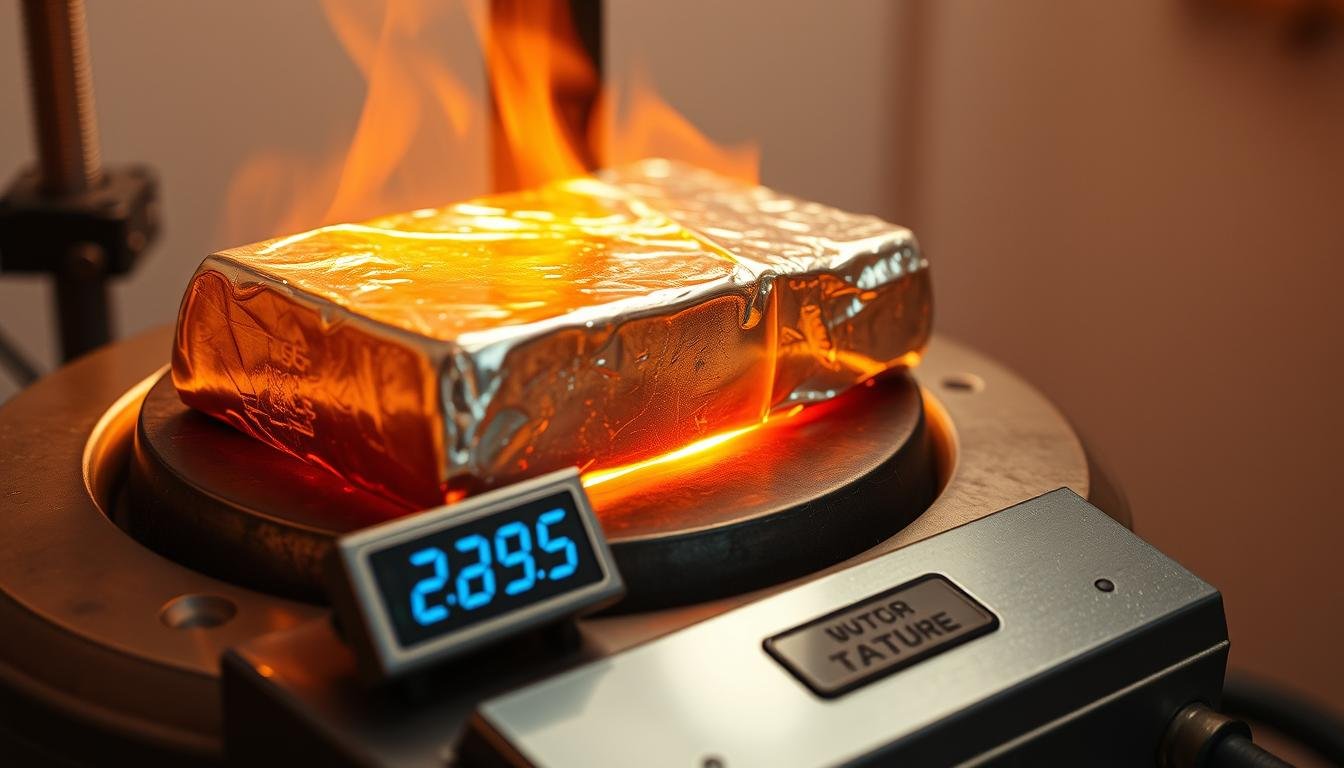
Understanding thermal properties of metals plays a critical role in modern manufacturing. For one widely used element, its specific phase-change temperature determines how engineers design products ranging from batteries to construction materials. This bluish-white metal, identified as atomic number 30 on the periodic table, transforms from solid to liquid at 419.5°C (787.1°F). Unlike many industrial … Read more